You can get alcoholic liver damage even if you don’t drink
By naturopath Margaret Jasinska
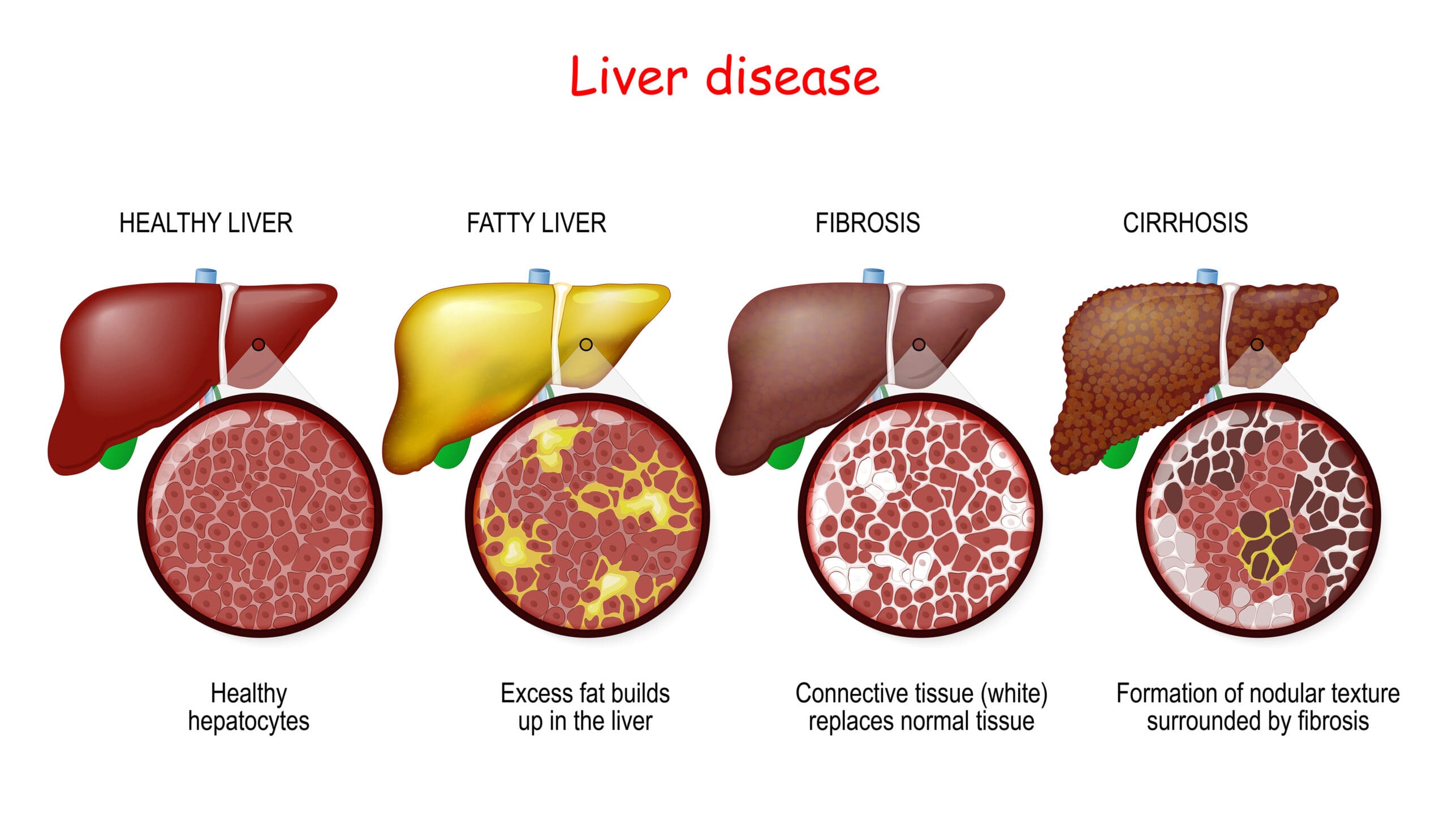
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the build up of fat in the liver caused by factors other than alcohol. It affects at least a quarter of the adult population in developed nations, usually by the time they are 40. The disease is becoming increasingly prevalent in children though and we’ve seen it in eight year olds.

What causes a fatty liver
Several things can cause fatty liver. These are the most common:
- Insulin resistance, pre-diabetes, type 2 diabetes
- High intake of sugar and carbohydrate-rich foods
- Intestinal diseases such as coeliac disease, inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome
- Autoimmune disease
- Viral infections
Recently, researchers have linked NAFLD to bad gut bacteria that produce large amounts of alcohol in the body. So far, this bacteria has been found in more than 60 percent of non-alcoholic fatty liver patients. These findings have been published September 19 in the journal Cell Metabolism.
According to lead study author Jing Yuan, “We were surprised that bacteria can produce so much alcohol. When the body is overloaded and can’t break down the alcohol produced by these bacteria, you can develop fatty liver disease even if you don’t drink.”
Yuan and other researchers discovered the link between specific gut bacteria and NAFLD when they saw a patient with severe liver damage and a condition called auto-brewery syndrome (ABS). People with ABS become drunk after eating sugar or refined carbohydrates. Having high levels of yeast in the gut, which can produce alcohol in the gut and lead to intoxication.
Yuan went on to say “We initially thought it was because of the yeast, but the test result for this patient was negative. Anti-yeast medicine also didn’t work, so we suspected [his disease] might be caused by something else.”
After they analysed the patient’s faeces, the researchers discovered he had several strains of the bacteria Klebsiella pneumonia in his intestines which produced high levels of alcohol. K. pneumonia is commonly found in low levels in the average person’s gut. However, the specific strains isolated from his gut can generate about four to six times more alcohol than strains found in healthy people.
After that, the team analysed the gut microbes from 43 fatty liver patients and 48 people with a healthy liver. They found around 60 percent of NAFLD patients had high or medium levels of alcohol-producing K. pneumonia in their gut, whereas only 6 percent of healthy people carried those strains.
We have around 1.5 kilograms of bacteria in our intestines. The types of bugs and quantities of those bugs can have an enormous influence on your health. Having the wrong gut bugs might give you digestive symptoms such as bloating, irritable bowel syndrome, reflux or gas, or you might get no symptoms at all. You might just develop the downstream manifestations of a gut problem, such as a fatty liver.
How many doctors check their patient’s gut bugs? It’s a lot easier to overcome a health problem if you can find out the cause and try to address that. It is easier to reverse a fatty liver if you correct gut bug problems. Having an excess of bad bacteria in your gut can be caused by eating foods high in sugar, or deficiency of stomach acid which is supposed to act as a disinfectant. You may have inherited the wrong bugs from your mother. Maybe you had several courses of antibiotics which was unavoidable because you had serious infections. Maybe you had food poisoning or gastroenteritis which affected the migrating motor complex in your intestines, leaving you prone to bacterial overgrowth. There are several reasons why a person can end up with bad gut bugs.
How can we correct the problem? A sugar free, low carbohydrate diet is helpful for restoring healthy gut bugs, but sometimes more powerful strategies are needed. Some people require a course of antibiotics, while others feel better with herbal remedies such as BactoClear capsules. They contain the herbal extract berberine, as well as essential oils of clove, oregano and thyme. They help to relieve symptoms of bloating, indigestion and medically diagnosed irritable bowel syndrome.
The books The Liver Cleansing Diet and Fatty Liver: You Can Reverse It both offer an enormous amount of information on how to reverse fatty liver and improve liver health.






Fascinating info.. thank you.