Do you know how diabetes affects the body?
By naturopath Margaret Jasinska
The incidence of diabetes is rising. Everyone is aware of that, yet not everyone understands the impact diabetes has on the body. Elevated blood sugar is extremely destructive to health. It has negative consequences immediately, as well as over the long term.
Diabetes type 1 is an autoimmune disease caused by the immune system attacking the insulin producing cells in the pancreas. Once these beta cells are destroyed, the pancreas can never produce enough insulin. This is a permanent disease but can still be helped with nutritional medicine and of course insulin therapy.
Diabetes type 2 is a disease that occurs when insulin is not working properly because the cells of the body have become resistant to it. In people with type 2 diabetes there is often too much insulin present in the body. The insulin does not work efficiently, so to compensate, the pancreas keeps on making more and more insulin.
The difference between diabetes type 1 and diabetes type 2 can be diagnosed with a 2-hour Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) where it is essential to measure both the levels of blood sugar and blood insulin after a load of glucose is given to the patient in a sugary drink. In both diabetes type 1 and diabetes type 2 the blood sugar rises too high. However, in diabetes type 1, the insulin levels remain low and inadequate, and in diabetes type 2 the insulin levels rise way too high. There are additional antibody blood tests that are done to confirm the presence of type 1 diabetes. In diabetes type 1, where insulin levels are inadequate, it is essential that the patient is prescribed insulin, as oral drugs do not work well. Insulin can be given as injections (which have a tiny painless needle) or the wonderfully effective insulin pump. This insulin therapy can control blood sugar levels very well and thus prevent the complications of diabetes.
When type 1 is diagnosed in adulthood, it usually comes on more gradually and is not as severe as type 1 diabetes in childhood. For this reason, it is usually referred to as LADA: Latent Autoimmune Diabetes of Adulthood. The incidence of this type of diabetes is rising sharply, and in fact some research has shown now more than half of type 1 diabetes is diagnosed in those over the age of 30.
Symptoms of diabetes
The following are all possible symptoms of diabetes:
- Increased hunger
- Increased thirst
- Fatigue
- Increased urination, particularly at night
- Sores that do not heal
- Infections such as thrush or skin infections such as boils or fungal skin infections
- Blurred vision
- Burning, numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Weight loss or weight gain
- Irritability and mood changes
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Erectile dysfunction
- Bell’s palsy and carpal tunnel syndrome. These conditions can both be a result of nerve damage caused by episodes of high blood sugar.

All those symptoms can be attributed to other health problems besides diabetes. If you suffer with a few on that list, please ask your doctor for a blood sugar test.
Potential complications of diabetes
Diabetes is a terrible disease; it can greatly reduce the quality of your life, make you more prone to several serious diseases and cut your life short prematurely. High blood sugar over a sustained period of time has many detrimental health consequences, therefore, the longer a person has diabetes, the worse the health consequences. The complications of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are usually the same.
You are probably well aware that diabetics are very prone to cardiovascular disease; in fact, people with diabetes are three to four times more likely to die of heart disease than non-diabetics, even if they have normal blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Diabetes is also a very common cause of kidney disease; this can result in the need for dialysis and an eventual kidney transplant. Diabetes causes disease of the large and small blood vessels, which impairs circulation of blood to organs and limbs; this can result in infections and the death of tissue, requiring an amputation.
The high blood glucose levels in diabetics can damage the nerves, resulting in gradual degeneration of the peripheral nerves, called neuropathy. This causes loss of sensation and weakness of the limbs. It can also cause bladder and bowel dysfunction. The better control you have over your blood glucose level, the less likely you are to experience diabetic complications.
Here are some other health conditions that diabetics are more prone to

Alzheimer’s disease
Studies have shown that compared to healthy people of the same age and sex, diabetics are twice as likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease. It is thought that the high blood sugar, combined with blood vessel damage contributes to dementia by impeding blood flow to the brain. In Alzheimer’s patients, amyloid protein builds up in the brain, while the same protein is deposited in the pancreas of type 2 diabetics. Most people with type 2 diabetes have excessive blood levels of insulin; too much insulin causes excessive inflammation in the body, which contributes to brain damage.

Diabetic retinopathy
This is the most common cause of blindness in Australians aged over 60 years. The longer you have been a diabetic and the higher your blood sugar, the more likely you are to experience eye damage. Diabetics are also at significantly increased risk of cataracts and glaucoma.
Kidney stones
People with diabetes are at greater risk of developing kidney stones, particularly uric acid kidney stones because they have very acidic urine. Obesity and insulin resistance are also associated with more acidic urine.

Sexual problems
The majority of males with diabetes experience low testosterone production, also known as hypogonadism. The symptoms of testosterone deficiency include erectile dysfunction, reduced sex drive, increased abdominal fat, reduced bone density and muscle tone, and depression. Damage to nerves and blood vessels in diabetics can result in reduced libido and ability to orgasm in both men and women. Diabetic women are more prone to chronic vaginal infections and difficulty with lubrication.
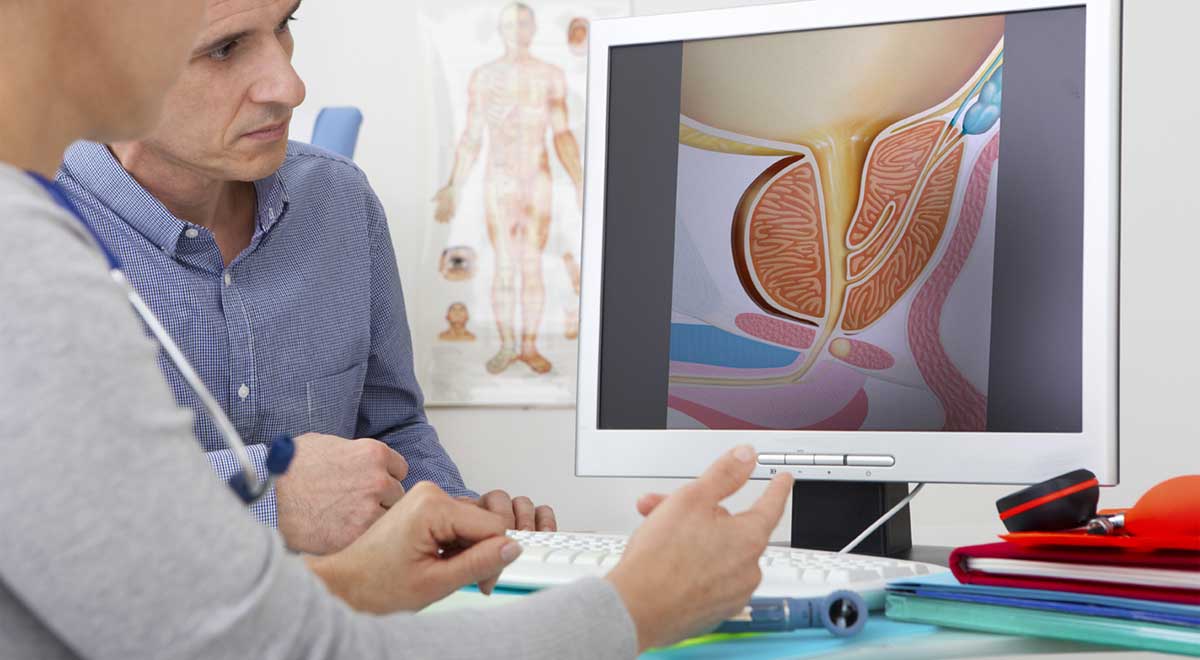
Enlarged prostate
Research has shown that diabetic men are more than twice as likely to experience BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) than non-diabetic men. The risk of BPH increases with obesity and elevated blood sugar.

Faster rate of ageing
According to medical research published in the medical journal The Lancet, “having diabetes is the clinical equivalent of aging 15 years”. One consequence is that diabetics are at greatly increased risk of fatal strokes and heart attacks much earlier in life. High blood sugar and insulin levels in type 2 diabetics promote inflammation and free radical damage to the body. Free radical damage to proteins such as collagen and elastin make you appear older.
If addressed early enough, the majority of type 2 diabetes can be reversed. You can read about how to do that in our book Diabetes Type 2: You Can Reverse It Naturally. If you are unhappy with your current eating habits, doing the Dr Cabot 15 Day Cleanse is a great way to establish a healthy routine and begin reclaiming your health.







Amazing detailed educational post.. thank you
Great information, thank you!