By naturopath Margaret Jasinska
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that develops in a location other than the uterus. Most commonly it occurs in the Fallopian tubes, but it may also occur in the cervix, in an ovary or in the abdominal cavity. Conception occurs when the sperm penetrates the egg in a Fallopian tube. Normally the fertilised egg then travels down the Fallopian tube and implants in the uterine wall.
Occasionally something goes wrong and this does not happen.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
In the initial stages, an ectopic pregnancy mimics the symptoms of a normal pregnancy. Most women experience a little morning sickness and breast tenderness. However, the following symptoms soon develop:
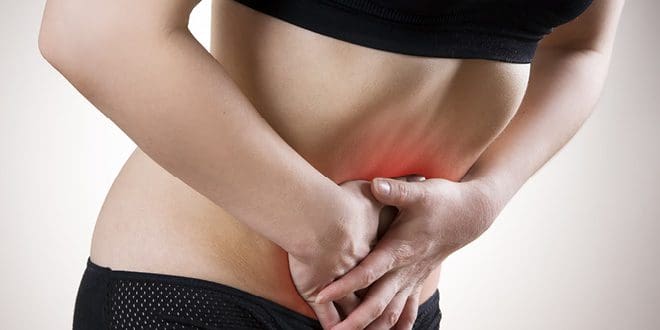
- Lower abdominal pain
- Lower back pain
- Cramps on one side of the abdomen
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting
- If a Fallopian tube ruptures there is severe pain in the lower abdomen. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate surgery.
Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy
Women who have struggled with infertility are at increased risk of having an ectopic pregnancy. It generally occurs when there is a blockage in a Fallopian tube, or the tiny hair-like structures (cilia) in the tubes cannot move the fertilised egg along properly. The following factors increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy:
- Previous infection of the pelvic organs and Fallopian tubes
- Endometriosis
- Reversal of a tubal ligation
- Surgery to remove the appendix
- Cigarette smoking. Smoking quadruples the risk of ectopic pregnancy. This is because it increases levels of a protein called PROKR1 in the fallopian tubes. This substance inhibits movement of the egg along the Fallopian tube.
Ectopic pregnancies that are detected at an advanced stage require surgery to remove the embryo and attempt to repair the Fallopian tube. In non-emergency cases, medication is usually given to induce a miscarriage. Women who have had one ectopic pregnancy are at risk of having another and often experience a large amount of anxiety about this.
An ectopic pregnancy can do a great deal of harm to your fertility, mainly through destruction of a Fallopian tube. Therefore, as soon as a blood test confirms you are pregnant, we strongly recommend you have an ultrasound to confirm that the embryo is developing in your uterus, where it should be.
For more information about fertility see our book Infertility: The Hidden Causes.







Leave A Comment