High blood sugar can age you prematurely
By naturopath Margaret Jasinska
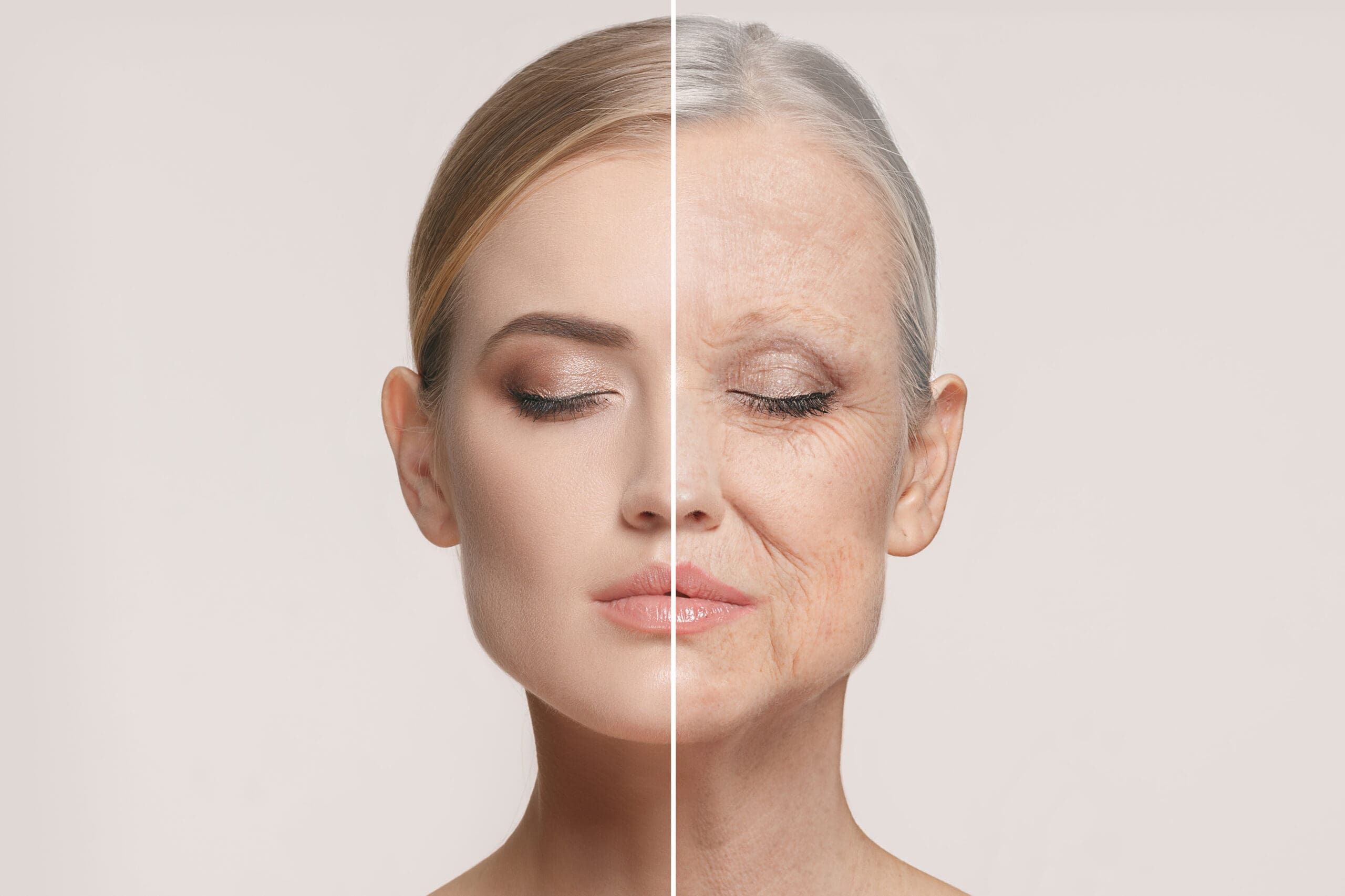
Did you know that elevated blood sugar can cause your skin to age more quickly? Consistently raised blood glucose, as well as occasional glucose spikes can accelerate a process in your skin called glycation. This is where glucose binds with protein and changes its structure. If glucose glycates the collagen in your skin, it can become rigid and sag prematurely. Your skin can lose its bounce and elasticity.
You don’t have to be a diabetic to suffer the damaging effects of high blood sugar. Research has shown that blood sugar much lower than that officially labelled diabetic still significantly harms your body and shortens your lifespan.
The incidence of diabetes is rising rapidly in every country on the planet. It is estimated there are currently more than 285 million people in the world with diabetes. By 2030 this figure is expected to leap to 439 million.
You are probably aware of the health consequences associated with diabetes: increased risk of heart attacks and strokes, blindness, kidney damage, nerve and blood vessel damage, dementia and erectile dysfunction.
What is normal blood sugar?
If you have ever had a fasting blood sugar test, you may know that the normal reference range is 3.6 – 5.4 mmol/L. If your fasting blood sugar is 5.5 mmol/L or higher, you are said to have insulin resistance (also called pre-diabetes, syndrome X or metabolic syndrome).
You would only be diagnosed as a diabetic if your fasting blood sugar reached 6.9 mmol/L or higher. Interestingly, research has shown that elevated blood sugar at not yet diabetic levels still creates enormous harm to your body.
A one off fasting blood sugar test is a very poor indicator of what your blood sugar level is 24 hours a day, seven days a week. It is a poor indicator of your glucose tolerance. A fasting blood test doesn’t indicate how high your blood sugar gets after a meal. New research has shown that blood sugar spikes after each meal can significantly raise your risk of heart attacks, strokes, eye damage and cancer, and speed your rate of ageing. If you eat sugar and high carbohydrate foods regularly, your blood sugar is probably spiking quite high after these meals. The longer your blood sugar is elevated, the more time it has to do damage to your body. Some people who eat a lot of sugar and grains have elevated blood sugar for a large part of the day. This may not be picked up by a fasting blood test.
A more reliable test that gives a better indicator of what your blood sugar has been day and night for the past three months is called a glycated haemoglobin test, also known as HbA1c. Your doctor can order this test and ideally your result should be below 5.5%.
Collagen
Collagen is the glue that holds your body together. The name collagen comes from the Greek language, meaning glue-producing. It’s a fibrous protein found right throughout your body. Your bones, joints, connective tissue, tendons, ligaments, nails and hair all contain collagen. Collagen is the main structural component of your skin; approximately 80 percent of your skin’s dry weight is collagen.
Getting collagen via your diet, or taking a collagen supplement will provide you with the protein building blocks your body needs in order to make collagen. Most of the collagen you ingest will be digested into its component amino acids. There are specific nutrients you require in order to rebuild collagen. These include vitamin C, zinc, copper, silica, sulphur and biotin. These nutrients are found in Collagen Food powder.
Why is sugar bad for your skin?
When you eat sugar or high glycaemic foods that are rapidly digested into sugar, your body breaks down these carbohydrates into glucose. This raises your blood insulin level. Simple carbohydrates, like sugar, most bread and soft drinks cause your insulin level to spike. A sudden rise in blood sugar and insulin cause acute inflammation in your body.
Inflammation leads to the production of enzymes that break down collagen and elastin, promoting sagging skin and wrinkles. The sugar in your bloodstream permanently attaches to the collagen in your skin via the process called glycation. Glycation causes stiffness, thus reducing elasticity and buoyancy in the skin. This damage occurs internally as well. Sugar can bind to almost any protein in your body. It can cause glycation in your blood vessels, your eyes and your kidneys. This is a reason why diabetics are prone to complications in these organs.
Along with increasing the effects of ageing, glycation can also aggravate skin conditions like acne and rosacea.
Recommendations for healthy blood sugar
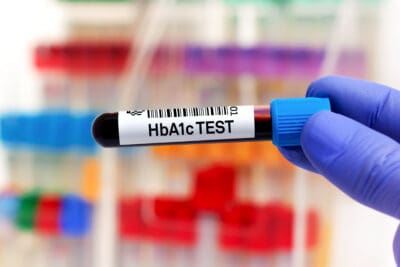
Get a blood test. A significant proportion of people with type 2 diabetes are undiagnosed, therefore if you have not had your blood sugar checked in the last two years, ask your doctor for a test. You should get a fasting blood sugar test and also an HbA1c test. Your blood sugar should be below 5.5 mmol/L and your HbA1c should be below 5.5%.

Reduce the amount of carbohydrate rich food you eat. Sugar, bread, pasta, rice, potatoes, breakfast cereals, sugary drinks and anything made of flour will all raise your blood glucose level after you eat them. The average person eats far too much of these foods. If you are carrying excess weight around your waist that is a great indicator your blood sugar level is probably climbing. Follow the lower carbohydrate, higher protein eating plan in our book Diabetes Type 2: You Can Reverse It Naturally
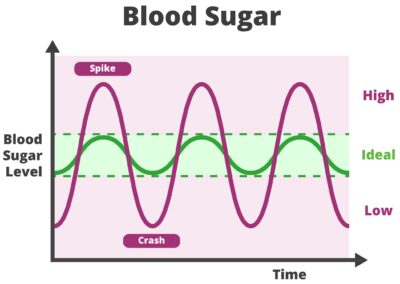
Keep your blood sugar level balanced throughout the day. It is important to avoid spikes in blood sugar after meals. You can achieve this by limiting the amount of carbohydrate you eat, exercising regularly and having some apple cider vinegar before or with meals. If you do eat a carbohydrate rich meal, adding protein, fat and fibre to the meal significantly reduces glucose spikes.
Look after your liver. A diagnosis of fatty liver often arrives years before a diabetes diagnosis. If your liver is unhealthy, you will have great difficulty controlling your blood sugar. It will rise too high and you’ll be prone to hypoglycemia and sugar cravings. Follow the recommendations in the book Fatty Liver: You Can Reverse It.

Try to get enough good quality sleep. Adults require 7.5 to 8 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. If you don’t get that, you are far more likely to gain weight and develop high blood sugar. Sleep deprivation raises the hunger hormones in your body and impairs the fat burning hormones. If you struggle to achieve good sleep, a magnesium supplement may help.








Leave A Comment